NVS/KVS/UGC-NET/EMRS/RAJASTHAN GR.2 & 3 - Unit 2 (Cataloguing) - "Physical and Inner Forms of Library Catalogue"
Physical and Inner Forms of Library Catalogue
Physical Form of Catalogue
On the basis of physical form the library catalogue is mainly divided into the following types.
👉Conventional Form
👉Non-Conventional Form
Conventional Form
- Printed book/Register Catalogue
- Sheaf Catalogue
- Card Catalogue
Non-Conventional Form
- Visible Index Form
- Micro Form Catalogue
- Machine Readable Catalogue
- Micro Form Catalogue
💨 Micro Fish
💨 Micro Card
💨 Micro Film
Conventional Form
1.Printed book/Register Catalogue/Book Catalogue
The catalogue in which catalogues entries are hand written or printed and bound into a volume is known as Register or printed or Book Catalogue.
In United States first book catalogue is Harvard catalogue which was published in 1723.Yale catalogue was brought out in 1745.
2.Sheaf Catalogue
A catalogue formed by sheets, slips, or card fastened in a binder that permits the insertion or new material. Slips are usually of 6"x4" size notched at the left hand side. Its first use was made by the University Library, Leydon, Holland in 1876.
It was improved by madam Ricci in 1891. J.D. Brown invented in 1892 adjustable sheaf catalogue. The modern form was invested by Arthur Lambert. It provides shelf locking wicket. It is usually used in public libraries of U.K. In this form some difficulties of Book or Printed catalogue are removed.
3. Card Form
It is currently the most prevalent physical form. 5x3 or 12.7x7.5 cm in card form. Making Entries on size cards is done.
In 1775, the card form was first used by Rogier for the catalogue of the Paris Academy of Science.
In United Kingdom its first use was made by Trinity College, Dublin in early 19th Century.
Non - Conventional or Modern Form
In the modern era, Modern technology has replaced some new form in place of card form, the details of which are as follows-
1. Visible Form
⃟ This form of catalogue is mostly used by commercial and industrial libraries.
⃟ It is arranged in such a way that the title of each is easy to read. Their size is 125x20 cm.
2. Microform Catalogue
⃟ In this, the catalogue of many books on a single card is converted into microform catalogue from the photographic method by technical equipment.
⃟ This Microform cannot be ready by the normal eyes. To read it, a "Micro Reader" is required, which converts the short form to Expanded to make it readable.
⃟ This microform of catalogue is stored in the form of microfilm or microfiche.
⃟ A micro film is one long reel. While microfiche is in the form of a type of transparent card. Thus the time of reader is saved in microfiche.
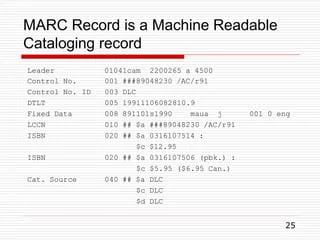
3. MARC [Machine Readable Catalogue]
⃟ The use of computer-generated catalogue has become common in developed countries since the 1960s. In 1966,for the first time in America, with the help of the Library of Congress, the Machine Readable Catalogue (MARC) scheme was started, which was completed in 1967.
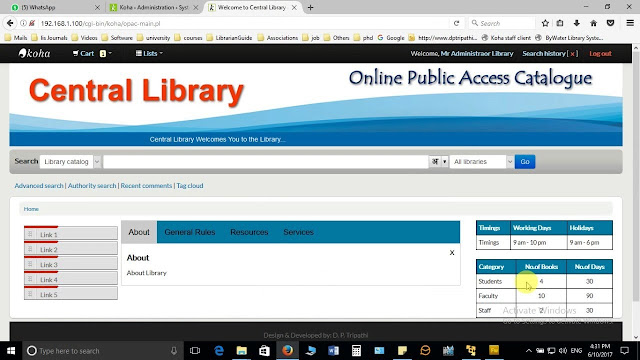
4. OPAC [Online Public Access Catalogue]
⃟ This is also a form of computerized catalogue. with the help of software available in the library, the catalogue of books is prepared in the computer. These the catalogue can be accessed from the various departments of the library on computer terminals. All these terminals are connected to the main server.
⃟ An online Database of material held by a Library or Group of Libraries to locate books and other materials available at Library is an OPAC.
⃟ Library of congress Developed OPAC cataloguing systems in the world.
⃟ The Card catalogues which were arranged in a specially designed catalogue cabinet are now being replaced by OPAC.






No comments
If you want to ask any question regarding blog, please ask. I will be glad to answer that